|
MimIR 0.1
MimIR is my Intermediate Representation
|
|
MimIR 0.1
MimIR is my Intermediate Representation
|
Introduces a type constructor %math.F for viarious IEEE-754 floating-point formats and a set of operations to calculate with instances of these types. All operations with the exception of %math.conv expect a Nat just in front of its actual argument. Here you can fine adjust via mim::plug::math::Mode how strictly you want to obey floating-point transformations.
A floating-point type with p many bits as precision and e many bits as exponent. The sign bit is neither included in p nor in e. Thus, the total number of bits occupied by a value of this type is p + e + 1.
Arithmetic operations.
Minimum and Maximum.
min or Maxi: Follows the behavior of libm’s fmin/fmax.
If either operand is a NaN, returns the other non-NaN operand. Returns NaN only if both operands are NaN. The returned NaN is always quiet. If the operands compare equal, returns a value that compares equal to both operands. This means that fmin(+/-0.0, +/-0.0) could return either -0.0 or 0.0.
I: Follows the semantics of minNum/maxNum specified in the draft of IEEE 754-2018.
If either operand is a NaN, returns NaN. Otherwise returns the lesser of the two arguments. -0.0 is considered to be less than +0.0 for this intrinsic.
| Subtag | Alias | N | M |
|---|---|---|---|
im | fmin | o | o |
iM | fmax | o | x |
Im | ieee754min | x | o |
IM | ieee754max | x | x |
Trigonometric and hypberbolic functions.
FF: sine, cosine, tangent, unusedHyperbolic counterpartArcus/Area counterpart (inverse)| Subtag | Alias | A | H | R | FF | Meaning | Semantics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ahff | sin | o | o | o | oo | sine | |
ahfF | cos | o | o | o | xo | cosine | |
ahFf | tan | o | o | o | ox | tangent | |
ahFF | o | o | o | xx | unused | - | |
aHff | sinh, h | o | x | o | oo | hyperbolic sine | |
aHfF | cosh | o | x | o | xo | hyperbolic cosine | |
aHFf | tanh | o | x | o | ox | hyperbolic tangent | |
aHFF | o | x | o | xx | unused | - | |
Ahff | asin , a | x | o | o | oo | arcus sine | |
AhfF | acos | x | o | o | xo | arcus cosine | |
AhFf | atan | x | o | o | ox | arcus tangent | |
AhFF | x | o | o | xx | arcus unused | - | |
AHff | asinh | x | x | o | oo | area hyperbolic sine | |
AHfF | acosh | x | x | o | xo | area hyperbolic cosine | |
AHFf | atanh | x | x | o | ox | area hyperbolic tangent | |
AHFF | x | x | o | xx | unused | - |
Power function: 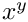
| Name | Meaning | Semantics |
|---|---|---|
%math.rt.sq | square root | |
%math.rt.cb | cube root |
Exponential function and logarithm:
LogarithmBB: natural, binary, decimal, unused| Subtag | Alias | L | BB | Meaning | Semantics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
lbb | exp | o | oo | natural exponential | |
lbB | exp2, bin | o | ox | exponential with base 2 | |
lBb | exp10, dec | o | xo | exponential with base 10 | |
lBB | unused | o | xx | - | unused |
Lbb | log | x | oo | natural logarithm | |
LbB | log2 | x | ox | logarithm with base 2 | |
LBb | log10 | x | xo | logarithm with base 10 | |
LBB | unused | x | xx | - | unused |
Error and complementary error function.
| Name | Meaning | Semantics |
|---|---|---|
%math.er.f | error function | |
%math.er.fc | complementary error function |
Gamma function and its natural logarithm.
| Name | Meaning | Semantics |
|---|---|---|
%math.gamma.t | gamma function | |
%math.gamma.l | natural logarithm of gamma function |
Absolute value of a floating point number
Common rounding operations for floating points:
floorceilroundtruncate| Name | Meaning | Semantics |
|---|---|---|
%math.round.f | round down | |
%math.round.c | round up | |
%math.round.r | round to nearest integer | |
%math.round.t | round towards zero |
Floating point comparison is made of 4 disjoint relations:
Unordered (yields true if either operand is a QNAN)GreaterLessEqual| Subtag | Alias | U | G | L | E | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ugle | f | o | o | o | o | always false |
uglE | e | o | o | o | x | ordered and equal |
ugLe | l | o | o | x | o | ordered and less |
ugLE | le | o | o | x | x | ordered and less or equal |
uGle | g | o | x | o | o | ordered and greater |
uGlE | ge | o | x | o | x | ordered and greater or equal |
uGLe | ne | o | x | x | o | ordered and not equal |
uGLE | o | o | x | x | x | ordered (no NaNs) |
Ugle | u | x | o | o | o | unordered (either NaNs) |
UglE | ue | x | o | o | x | unordered or equal |
UgLe | ul | x | o | x | o | unordered or less |
UgLE | ule | x | o | x | x | unordered or less or equal |
UGle | ug | x | x | o | o | unordered or greater |
UGlE | uge | x | x | o | x | unordered or greater or equa |
UGLe | une | x | x | x | o | unordered or not equal |
UGLE | t | x | x | x | x | always true |
Conversion between floating point and index types - both signed and unsigned - of different sizes.
Standard logistic function of a floating point number ( 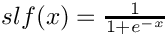
Reciprocal of the square root (